Hyperpigmentation vs Hypopigmentation: Understanding the Differences and Causes
Skin pigmentation is the natural color of the skin, which is determined by the amount of melanin present in the skin cells. Melanin is a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes, which is responsible for giving color to the skin, hair, and eyes. However, certain conditions can lead to an imbalance in the production of melanin, leading to either hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation. In this article, we will discuss the differences and causes of hyperpigmentation vs hypopigmentation.
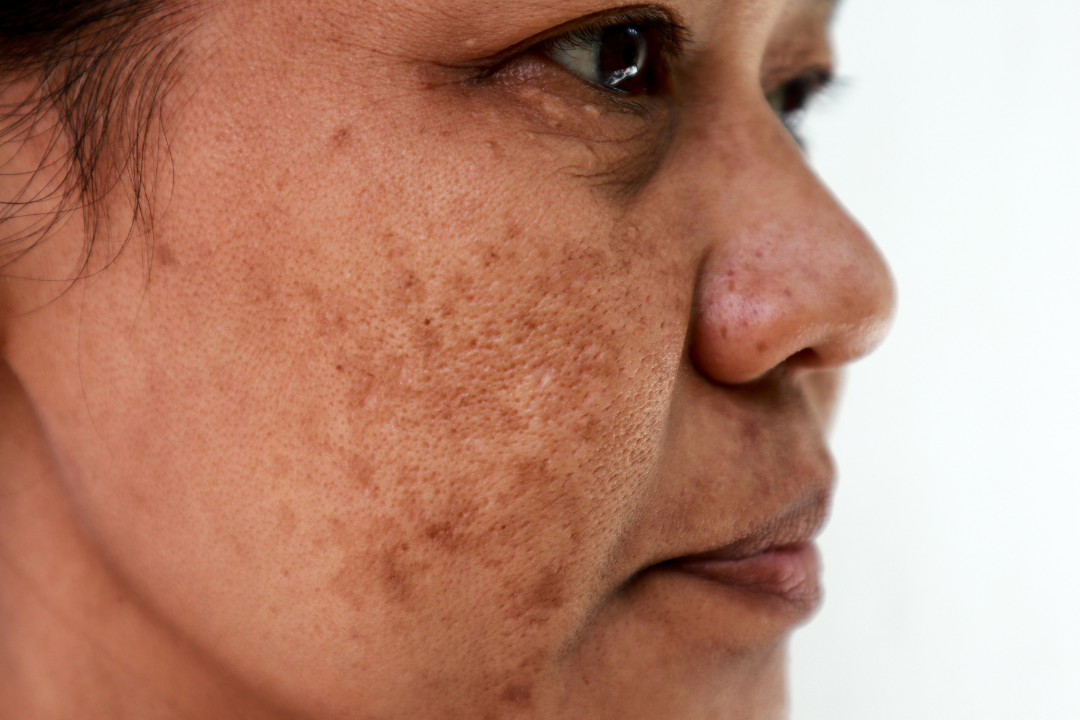
Hyperpigmentation refers to the condition where patches of skin appear darker than the surrounding skin due to an excess of melanin. This condition can occur in any part of the body, including the face, neck, arms, and legs. There are several causes of hyperpigmentation, including sun damage, hormonal changes, acne, certain medications, and skin injuries. One of the most common causes of hyperpigmentation is sun damage, which occurs due to prolonged exposure to the sun's harmful UV rays. Hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause can also lead to an increase in melanin production, causing hyperpigmentation. In some cases, hyperpigmentation can also be a side effect of certain medications, such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Hypopigmentation, on the other hand, is a condition where patches of skin appear lighter than the surrounding skin due to a decrease in melanin production. This condition can also occur in any part of the body, and its causes include genetic disorders, autoimmune diseases, and skin infections. One of the most common causes of hypopigmentation is vitiligo, which is a chronic autoimmune disorder that leads to the destruction of melanocytes, resulting in the loss of skin color. Another cause of hypopigmentation is albinism, which is a genetic disorder that affects the production of melanin, resulting in a complete lack of pigmentation in the skin, hair, and eyes.
The treatment for hyperpigmentation vs hypopigmentation varies depending on the underlying cause. In the case of hyperpigmentation caused by sun damage or hormonal changes, topical creams and serums containing hydroquinone or kojic acid can help to lighten the skin. Laser therapy and chemical peels can also be effective in reducing the appearance of hyperpigmentation. In the case of hypopigmentation caused by vitiligo or albinism, treatment options include topical corticosteroids, light therapy, and skin grafting.
In conclusion, hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation are two common skin conditions that affect people of all ages and skin types. Understanding the differences and causes of these conditions is essential in determining the appropriate treatment options. If you notice any changes in your skin's pigmentation, it is important to consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. With proper care and treatment, you can achieve healthier, more even-toned skin.